The Essentials of Distributed Cloud Computing
Current business organizations measure and oversee immense measures of information consistently. They require the cloud-based capacity to keep essential information free from any harm. Cloud stockpiles give endeavor versatility and skill to record crucial business data. Cloud administrations affix the whole organization work process by building more proficient systems, making new current methods of associating with clients, adapting, etc. The circulated cloud is additionally characterized as a tech pattern by Gartner for 2021.
The circulated cloud model gives a scope of gainful provisions for endeavors, and we will discuss the more significant part of them further in this article.
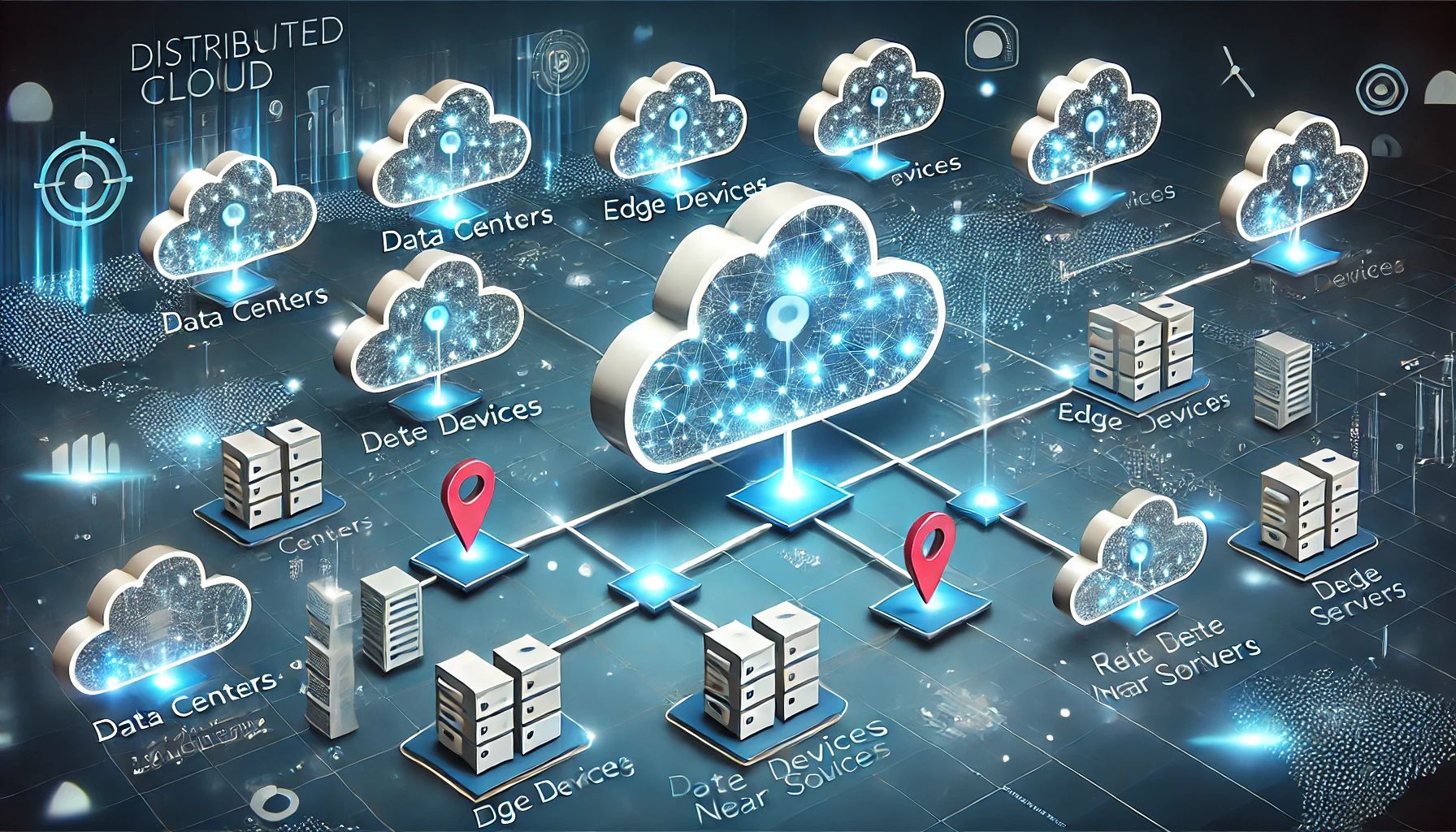
A disseminated cloud is a sort of cloud that has a geologically scattered foundation that runs administrations at the organization’s edge.
This is not the same as the hypothetical cloud model that depends on an incorporated server farm.
With an appropriated cloud model, associations diminish inactivity, network blockage, and the hazard of information misfortune. Moreover, associations can more readily guarantee consistency with information power guidelines since information can be kept in the country in which it was created.
Distributed Cloud: The Future of Public Computing
Imagine running your public cloud infrastructure across multiple locations—not just on your cloud provider’s network, but also on-premises, in other cloud providers’ data centers, or third-party colocation facilities. Distributed cloud makes this a reality, allowing you to manage everything seamlessly from a single control plane.
With this strategically managed distribution of public cloud services, your business can deploy and run applications or individual components in a mix of cloud environments that best meet your performance, compliance, and other needs. Distributed cloud addresses the operational and management inconsistencies often found in hybrid or multi-cloud setups.
Moreover, distributed cloud is the ideal foundation for edge computing, enabling applications and servers to run closer to where data is generated.
The demand for distributed cloud and edge computing is largely driven by the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), telecommunications, and other data-intensive applications that require real-time processing. Additionally, distributed cloud helps businesses navigate the challenges of adhering to country or industry-specific data privacy regulations. More recently, it has provided essential IT services to employees and end-users impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Embrace the future with distributed cloud, where flexibility, performance, and compliance meet seamlessly.
How Appropriated to Distribute Cloud Functions
You might have known about appropriated processing, in which application parts are spread across various organized PCs and speak with each other through informing or APIs, fully intent on further generally developing application execution or augment figuring proficiency.
Appropriated cloud goes a monster above and beyond by disseminating a public cloud supplier’s whole register stack to any place a client may require it – on-premises in the client’s server farm or private cloud, or off-premises in at least one public cloud server farms that might have a place with the cloud supplier.
Essentially, dispersed cloud broadens the supplier’s unified cloud with topographically circulated miniature cloud satellites. The cloud supplier holds focal power over all appropriate frameworks’ tasks, refreshes, administration, security, and unwavering quality. Furthermore, the client gets to everything – the concentrated cloud administrations and the satellites any place they are found – as a solitary cloud and oversees everything from a lone control plane. Like this, as industry expert Gartner puts it, dispersed cloud fixes with crossover cloud and half breed multicolored breaks.
Sorts of Distributed Cloud
Public-asset registering:
• This sort of appropriated cloud is an aftereffect of a broad meaning of distributed computing as it is more identify with conveyed processing than distributed computing. This is additionally considered as a sub-class of distributed computing.
Volunteer cloud:
• This kind of processing is described as the crossing point of distributed computing and public-asset figuring. In this sort, a distributed computing framework is construct utilizing chipped-in assets. In any case, in this sort of framework, many difficulties emerge because of the unpredictability of the assets that are using to assemble it and the unique climate in which it works. It is likewise called shared mists or impromptu mists.
Advantages of distributed cloud
• Distributed distributed computing offers reiteration and constancy, a geo-replication that empowers in lessening the expense.
• Distributed cloud likewise offers quick come-up short overs with the assistance of far-off imitations that can in a flash reset in the event of fizzling.
• Distributed cloud decreases wide-region traffic. By utilizing the assets given by appropriated cloud, wide-region correspondence can be reduced.
• Distributed cloud permits breaking complex issues and information into more modest pieces and has different PCs that can be worked upon equally.
The worth of disseminated distributed computing
Cloud administrations from public cloud suppliers become “disseminated” out to explicit and changed actual areas. Activities being truly nearer to the people who need the abilities empower the low-idleness process. This likewise guarantees a reliable control plane to manage the public to private cloud framework and expand reliably across the two conditions. Taken together, these things can convey significant enhancements in execution because of the disposal of dormancy issues, just as decrease the danger of worldwide organization-related blackouts or control plane failures.
Appropriate cloud will advance in two unmistakable stages. Stage One will comprise the like-for-like mixture.
Conveyed cloud makes deliberately positioned substations of cloud register, stockpiling, and systems administration that can go about as shared cloud pseudo accessibility zones. Gartner utilizes the expression “substations” to summon the picture of auxiliary stations, for example, branch mail depots, where individuals assemble to utilize administrations.
Since appropriated cloud substations are the obligation of the starting public cloud supplier, the key cloud incentives of usefulness, development, and backing stay flawless. By 2024, most cloud administration stages will give some dispersed cloud benefits that execute at the mark of need.
Other explicit benefits of appropriated cloud possibly include:
• Increased consistency with administrative necessities that information should be in a particular client area
• Reduced network disappointment hazard because the cloud administrations can dwell in nearby or semi local subnets, permitting them to work discontinuously untethered
• A emotional expansion in the number and accessibility of areas where cloud administrations can be facilitated or from which they can be devoured (register zones)
Distributed Cloud Defeats Crossover Challenges.
One test Gartner refers to in a report contrasting circulated cloud and half breed cloud is that a few associations that believe they’re carrying out crossover cloud aren’t. In particular, they’re utilizing public cloud benefits, yet they’re not using private cloud innovations.
When undertakings have genuine crossover conditions, they run into difficulties since private and public clouds are two distinct executions that should be overseen independently. The subsequent overhead expenses the worth crossbreed cloud conveys.
There are presently half-breed cloud contributions that address the many difficulties Gartner refers to in its report. However, designers and IT pioneers need to keep the limits of crossbreed cloud in context.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IT cloud computing is revolutionizing how businesses manage their infrastructure by offering unprecedented flexibility and scalability. With the advent of distributed cloud, organizations can leverage public cloud services across diverse locations, including on-premises and third-party data centers.
This approach not only enhances performance and regulatory compliance but also simplifies the complexities often associated with hybrid and multi-cloud environments. By adopting distributed cloud, businesses can ensure their applications and services are optimally deployed, providing a seamless and efficient user experience.

