Every day, vast amounts of data are structured, managed, and protected online using various software tools. Different processes require specific software: one for structuring data, another for managing it, and yet another for protection. Here, we’ll focus on the technology that protects online user data: Privacy-Enhancing Computing.
What is Privacy Enhancing Computing?
Privacy Enhancing Computing (PEC) doesn’t have a single, universally accepted definition. However, it can be described as technology that minimizes personal data usage and maximizes data security. PEC ensures that online user data remains private and secure in the applications and services where it’s used. In today’s digital age, where data privacy violations are increasing, PEC plays a crucial role.
Why Privacy Enhancing Computing Matters?
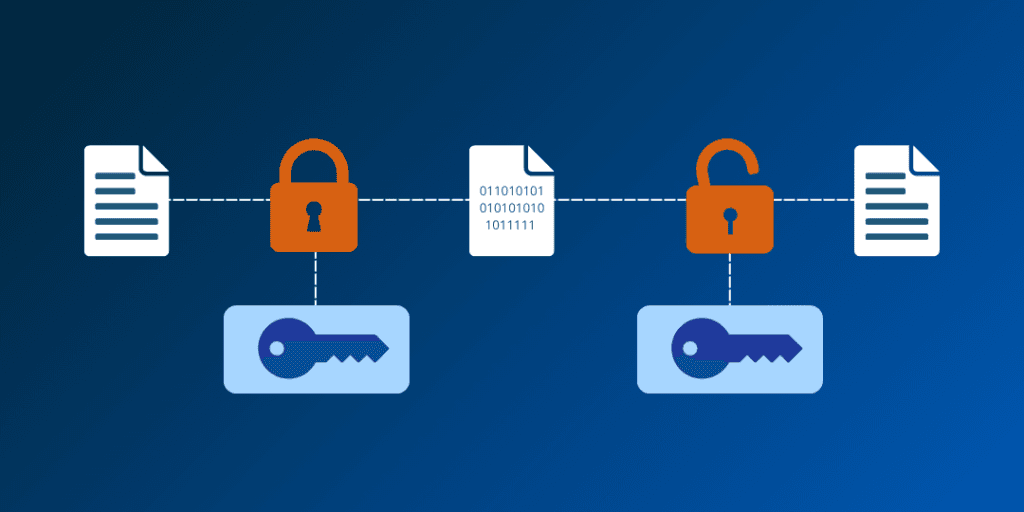
As technology advances, so do the threats to data privacy. A significant 82% of websites refuse to share user data with third parties for protection purposes, but 18% still do.
Privacy Enhancing Technology not only protects data but also ensures it remains confidential when processed by third parties. This technology minimizes personal data usage without compromising system functionality. It’s the responsibility of every site and organization to protect user data, thereby gaining their trust.
Objectives of Privacy Enhancing Computing
- Enhance Privacy Protection: PEC aims to enhance privacy protection by controlling personal data sent and used by online organizations for merchant purposes.
- Ensure Data Confidentiality: PEC keeps user data confidential, even when processed by third parties.
- Gain User Trust: By implementing Privacy Enhancing Technology, websites can assure users their data is safe, thereby gaining their trust.
Types of Privacy Enhancing Technology
- Functional Privacy Technology: Focuses on minimizing personal data usage.
- Hard Privacy Technology: Provides robust protection measures to ensure data confidentiality.
The Role of PEC in the Internet Age
The internet is a powerful tool, but it can also be used for surveillance. Privacy protection laws enable individuals to use appropriate tools, and PEC aims to protect individual data strictly. Types of Privacy Enhancing Technology
provides:
- A trusted environment for processing private data without exposure.
- Privacy-aware analytics using machine learning.
- Algorithms and data transformation through homomorphic encryption.
- Evaluation of services and organizational reliability.
Challenges in Implementing Privacy Enhancing Computing

Implementing PEC in business can be challenging and time-consuming. According to a 2021 study by Anastasiia Mikula, 27% of users still don’t trust online channels with their data, often using fake identities to register. This indicates a significant lack of trust in online data protection tools.
Reasons to Implement Privacy Enhancing Technology
- User Trust: Users need assurance that their data is confidential.
- Data Protection: Merchants and third parties often have access to user data. PEC ensures this data remains confidential, gaining user trust.
- Mandatory Protection: Websites without PEC are seen as insecure. The absence of PEC can lead to privacy breaches and long-term harm.
Trends in Privacy Enhancing Technology
- Homomorphic Encryption: Encrypts data so it can be processed without being decrypted.
- Trusted Execution Environment (TEE): Provides a secure area of the main processor to ensure code and data loaded inside are protected.
- Multi-Party Computation (MPC): Allows multiple parties to jointly compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private.
- Differential Privacy: Ensures that the removal or addition of a single database item doesn’t significantly affect the outcome of any analysis.
- Personal Data Stores: Allow users to store their personal data securely and control access to it.
- Obfuscation: Makes data unintelligible to unauthorized users.
Importance of PEC for Enterprises
Enterprises prioritize data protection and privacy. Privacy Enhancing Technology makes it easier and more convenient for them to achieve this. It is used in various sectors, including:
- Business Companies: Protecting customer data like phone numbers, emails, photos, and addresses.
- Finance Companies: Securing bank account details to prevent harm from hacking.
- Healthcare Companies: Safeguarding patient information to track health securely.
- Social Media Platforms: Ensuring user information remains confidential during registration and use.
Trends in Privacy Enhancing Technology

Privacy enhancing technology (PET) is evolving to address data privacy and security concerns. Key trends include:
- Homomorphic Encryption: Allows encrypted data to be processed without decryption, ensuring continuous protection.
- Trusted Execution Environment (TEE): Secure processor areas that protect sensitive code and data.
- Multi-Party Computation (MPC): Enables multiple parties to jointly compute functions while keeping their inputs private.
- Differential Privacy: Adds noise to data sets to protect individual privacy during data analysis.
- Personal Data Stores (PDS): Allow individuals to securely store and control access to their personal data.
- Obfuscation: Makes data unintelligible to unauthorized users through masking, tokenization, and encryption.
- Federated Learning: Trains machine learning models across decentralized devices without sharing raw data.
- Secure Multi-Party Analytics: Uses MPC to allow collaborative data analysis without revealing individual data sets.
- Blockchain for Data Privacy: Provides decentralized, tamper-proof data storage for secure data sharing.
- Privacy-Preserving AI: Develops AI systems that protect data privacy using techniques like differential privacy and federated learning.
These advancements enhance data privacy and security, allowing for more responsible and secure data usage.
Importance of Privacy Enhancing Computing for Websites
- User Trust:
- Building Confidence: Assures users their data is safe, fostering loyalty.
- Retention: Trustworthy websites attract and retain users.
- Data Protection:
- Preventing Breaches: Keeps personal data secure.
- Compliance: Helps meet data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA.
- Confidentiality and Security:
- Third-Party Processing: Ensures data remains private even with third-party handling.
- Encryption: Protects data from unauthorized access.
- Minimizing Risks:
- Reducing Vulnerabilities: Lowers risk of cyberattacks.
- Mitigating Damage: Limits potential damage in case of security incidents.
- Competitive Advantage:
- Differentiation: Attracts privacy-conscious users.
- Reputation: Positions website as a leader in data security.
- User Control:
- Empowering Users: Gives control over personal data.
- Transparency: Builds trust through clear privacy practices.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Avoiding Penalties: Prevents fines for non-compliance.
- Future-Proofing: Keeps up with evolving privacy regulations.
- Enhanced User Experience:
- Seamless Protection: Maintains high security without compromising usability.
- Transaction Trust: Ensures secure online transactions.
Conclusion
Privacy Enhancing Computing has transformed how organizations protect user data. By minimizing personal data usage and maximizing security, PEC not only protects data but also builds user trust. Implementing PEC is essential for any website or organization that values user privacy and data security.


Pingback: What Is Digital Trust Technology? What Is Digital Trust Technology