As technology advances, the realm of printing is expanding beyond the capabilities of traditional 3D printers to embrace the innovative concept of 4D printing. While 3D printers have revolutionized manufacturing by creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer, 4D printers add a new dimension: time.
This transformative approach allows objects to change their shape or function after printing in response to environmental stimuli. In this article, we delve into the fundamentals of 4D printers, exploring how they differ from their 3D counterparts and the groundbreaking applications they offer.
What Is a 4D Printer? Understanding Its Principles and Differences from 3D Printing
While 3D printers are becoming increasingly widespread, research into the emerging technology of 4D printers is ongoing. A 4D printer introduces the “time dimension” to 3D printing, which may sound like magic or mere hype at first glance. This article will clarify what a 4D printer is, how it operates, and how it differs from a 3D printer.
Basics of Shape Memory Materials in 4D Printing

3D printers use additive manufacturing technology, employing liquid resins that harden with light (UV or other types). This has revolutionized manufacturing processes, enabling the production of highly durable items using materials like carbon or metal. However, if materials that can change shape post-printing are used, this capability greatly enhances manufacturing, particularly in extreme environments like space. This concept underpins 4D printers.
The core idea revolves around “shape memory.” Some materials change shape under specific conditions, such as heat or light. For example, shape memory alloys return to their original form when exposed to a particular temperature, a phenomenon discovered in 1951. These materials, such as springs, loops, and eyeglass frames, have been used in various applications since the 1980s. Similarly, polymers, including plastics and elastics, exhibit shape memory due to “crosslinking” within their structures.
What Can a 4D Printer Do?

4D printers builds on the principles of shape memory by incorporating a time factor into the printing process. MIT researcher Skyler Tibbits introduced the concept of 4D printing in 2013, with his TED talk “4D Printing That Changes the World.” Other institutions, including Harvard University and the University of Illinois, have received significant funding to explore 4D printing.
4D printing enables materials to self-assemble and change shape over time in response to environmental stimuli. This technology allows the creation of structures that transform or adapt their shapes after printing, using materials with shape memory properties.
Challenges and Innovations in 4D Printing
One significant challenge in 4D printing is the development of shape memory polymers suitable for 3D printing. Different 3D printing methods, such as stereolithography and FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling), require specific material properties. For instance, in FDM, the material must have minimal shrinkage to maintain shape accuracy after cooling.
3D printing technology has evolved significantly since its inception in 1983. The availability of affordable 3D printers and advanced design software has made it accessible for a wide range of applications. Despite the advantages of 3D printing, such as material and energy efficiency, 4D printers promises even greater potential by introducing time-dependent material transformations.
The Future of 4D Printing
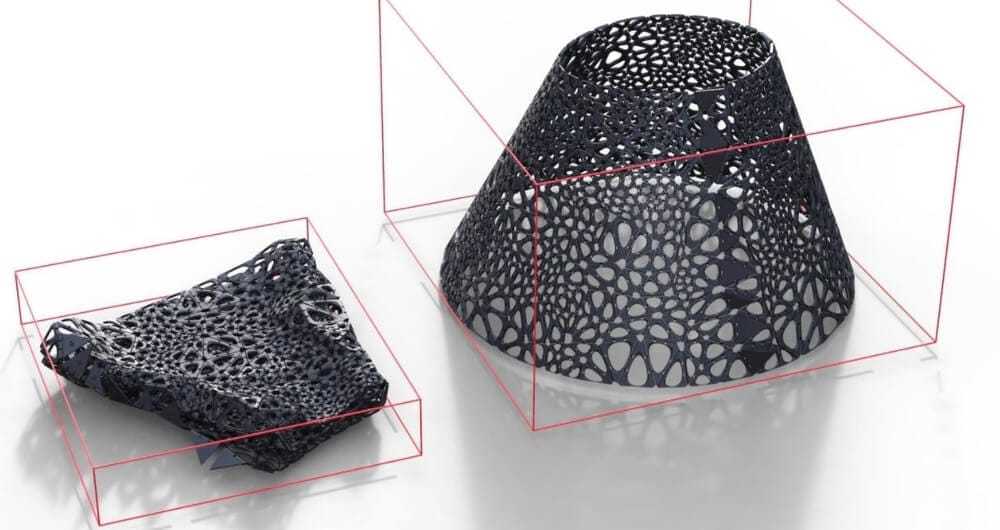
In 4D printing, the design process is crucial as it integrates time into the 3D printed object. 4D printed structures must be engineered to utilize smart material deformation mechanisms that change over time. This technology leverages the self-assembly behavior of materials in response to heat, UV, and moisture. For example, temperature-responsive materials, like thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), can be used to create adaptive prosthetics that react to temperature changes.
As 4D printing continues to develop, it holds promise for creating innovative materials and structures that evolve and adapt over time, expanding the possibilities of what can be achieved with additive manufacturing technologies.
Read More
- What Is 6G?
- Top 6 New Technology Trends for 2024
- Exploring the Future of Cutting Edge Technology
- What Is Gaming Processor and how It Works?