In today’s data-driven world, businesses are inundated with vast amounts of information from a multitude of sources. Traditional data management systems, which often operate in silos, struggle to keep up with the increasing complexity and volume of data.
Enter data fabric – a revolutionary approach that weaves together disparate data sources into a cohesive, unified network. This innovative architecture not only simplifies data management but also enhances accessibility, governance, and security, enabling organizations to make more informed, data-centric decisions. By integrating data across various platforms, data fabric eliminates bottlenecks and fosters a more agile and responsive business environment.
Strategy to Maximize Current and Future Data Investments
Leveraging the entire data estate isn’t about a single technology but a comprehensive network of data. This network facilitates end-to-end assimilation of diverse data clouds and pipelines through automated and intelligent systems. Over the past decade, advancements in Artificial Intelligence, Hybrid Cloud, Edge Computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) have driven exponential data growth, increasing complexity for businesses.
As a result, data management and unification have become critical priorities, though challenges like decision-making bottlenecks, data silos, and security risks persist. Data fabric solutions address these issues head-on by integrating disparate information systems, enhancing security and governance, and increasing data accessibility for business users.
Holistic Data Centric Decision Making
Data fabrics enable a more integrated approach to decision-making. Traditionally, businesses had multiple data platforms tailored to specific functions, such as HR, supply chain, and customer data, which often operated in isolation.
Data fabrics allow leaders to view this information cohesively, providing a comprehensive understanding of the customer lifecycle and uncovering connections previously unnoticed. By bridging these gaps, its accelerate digital transformation and automation across organizations.
The Role of Data Visualization in Data Fabric
Data visualization is essential for data implementation. It involves ETL (extract, transform, and load) processes to connect visualization tools with various data sources, facilitating better insights and decision-making.
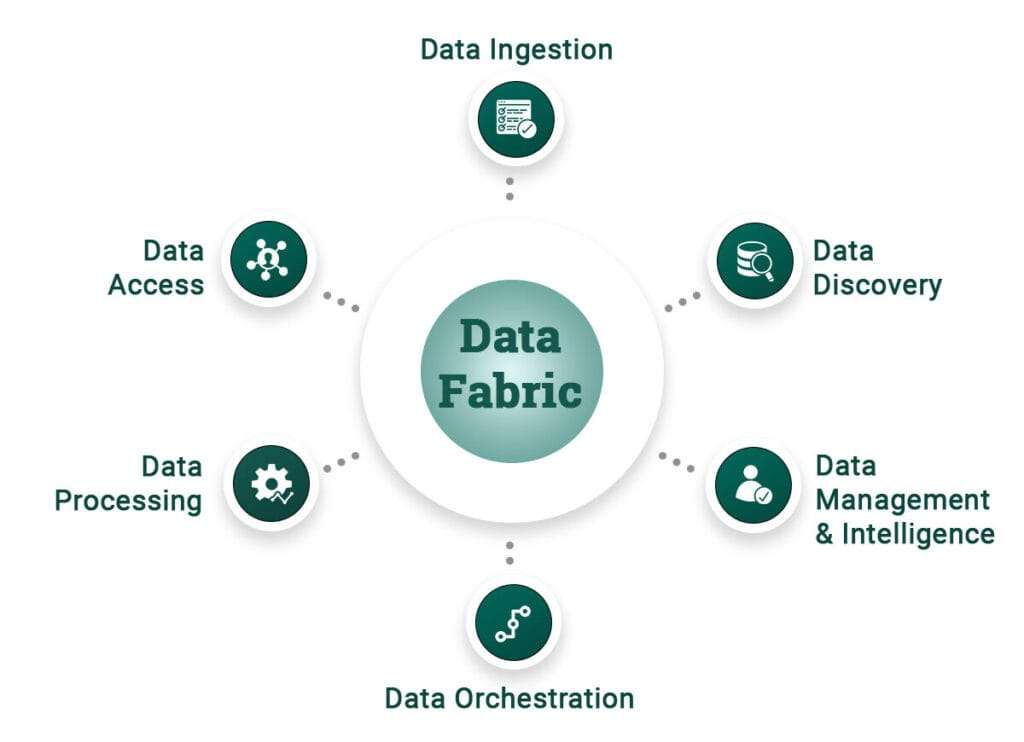
Understanding Data Fabric Architecture
Data fabrics consolidate data from legacy systems, data lakes, data warehouses, SQL databases, and applications through data services and APIs, offering a unified view of business performance.
Unlike traditional data storage systems, its aim to create fluidity across data environments, countering the problem of data gravity, where data becomes harder to move as it grows. They abstract technological complexities, making data movement, transformation, and integration seamless across the enterprise.
Key Components of Data Fabric Architecture
- Data Management Layer: Ensures data governance and security.
- Data Ingestion Layer: Connects cloud data, finding links between structured and unstructured data.
- Data Processing Layer: Refines data to surface relevant information.
- Data Orchestration Layer: Transforms, integrates, and cleanses data for business use.
- Data Discovery Layer: Identifies new opportunities to connect disparate data sources.
- Data Access Layer: Facilitates data consumption, ensuring proper permissions and compliance, and provides relevant data through dashboards and visualization tools.
Advantages of Data Fabric Architectures
According to Gartner, data fabrics improve efficiency by reducing integration design time by 30%, deployment by 30%, and maintenance by 70%. They offer several key benefits:
- Intelligent Integration: Utilizes semantic knowledge graphs, metadata management, and machine learning to unify diverse data types and endpoints, eliminating silos and improving data quality.
- Data Democratization: Expands data access beyond technical teams, allowing business users to make faster decisions and freeing up technical resources for more specialized tasks.
- Enhanced Data Protection: Implements robust data governance controls, ensuring secure access to sensitive data through masking and encryption, mitigating risks of data breaches.
Use Cases of Data Fabrics
Although still in early adoption, data fabrics excel in data integration, aiding businesses in data discovery and creating holistic customer views. This capability has proven particularly valuable in sectors like banking. its enable:
- Holistic Customer Insights: Integrating various data sources to provide a comprehensive view of customers, enhancing marketing and service strategies.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining data processes and reducing silos, leading to more efficient operations.
- Advanced Analytics: Supporting complex data analysis and machine learning models by providing unified and high-quality data.
In summary, data fabrics are transforming how businesses manage, integrate, and utilize data, driving more informed decision-making and operational efficiency.