Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that combines cryptographic techniques across multiple computers, forming a distributed network. This system records transaction information and other data in a synchronized manner.
Named for its structure, a blockchain collects transaction data in blocks over a certain period, verifies them, and connects them in a chain-like format. Also known as a Distributed Ledger, blockchain is the foundation of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
How Blockchain Technology is Beneficial for Today’s World
Blockchain technology offers numerous benefits that are transforming various industries. Here are some key advantages:
1. Enhanced Security
Blockchain’s decentralized and cryptographic nature makes it highly secure. Transactions are verified by multiple nodes, making it nearly impossible for hackers to alter data without being detected.
2. Transparency
Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger, allowing all participants to view the history. This transparency builds trust among users and reduces the risk of fraud.
3. Cost Efficiency
By eliminating the need for intermediaries, blockchain reduces transaction costs. This is particularly beneficial in industries like finance and supply chain management, where intermediaries are typically required to verify and process transactions.
4. Speed and Efficiency
Blockchain streamlines and automates transactions, reducing the time needed to complete them. This is especially useful in international trade and financial transactions, which traditionally take days to process.
5. Decentralization
Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, removing the need for a central authority. This decentralization enhances security and resilience, as there is no single point of failure.
6. Improved Traceability
In supply chains, blockchain provides an immutable record of product journeys. This traceability helps prevent fraud, ensures authenticity, and improves efficiency in recalling defective products.
7. Enhanced Privacy
Blockchain can offer enhanced privacy compared to traditional systems. While transactions are transparent, personal information can be kept private, providing a balance between transparency and privacy.
8. Innovation and New Business Models
Blockchain enables new business models and applications, such as decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and smart contracts, which automate and enforce contract terms.
9. Financial Inclusion
Blockchain technology can provide financial services to unbanked populations, offering them access to banking, loans, and other financial services through decentralized platforms.
10. Sustainability
Blockchain can support sustainability efforts by tracking and verifying environmental impacts, such as carbon emissions and resource usage, promoting eco-friendly practices.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Awareness
Interestingly, 60% of people familiar with virtual currencies do not know about blockchain, as revealed by a blockchain white paper survey.
Key Features of Blockchain
Blockchain’s standout feature is its resistance to data tampering. Even if transaction data is altered on some computers, the majority vote from other computers ensures the correct data prevails, preventing falsification and illegal transactions.
This decentralized approach means there’s no need for a central authority or large scale data management, making it a cost-effective solution. The reliability of transaction data is maintained without requiring a specific administrator.
How Blockchain Technology Works
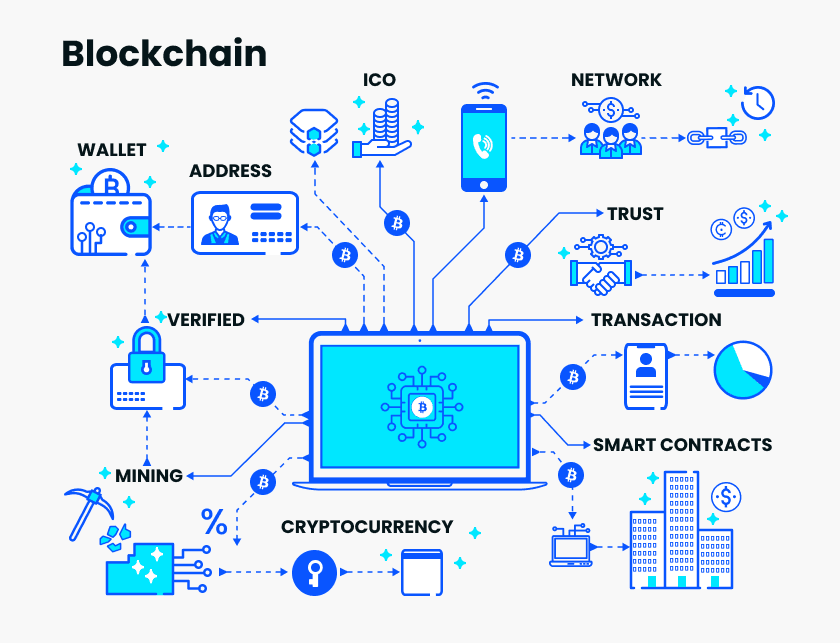
Blockchain technology creates a database by generating blocks of data and linking them in a chronological chain. Each block contains a hash value, a unique code generated by a hash function, that links it to the previous block. This allows the entire chain to be traced back through these hash values.
Robust and Secure Data Structure
Blockchain’s security is bolstered by its structure. If someone tries to alter information in a previously generated block, the hash value changes. This necessitates changing the hash values of all subsequent blocks, making tampering practically impossible. Thus, blockchain ensures a tamper resistant data structure.
Technologies Behind Blockchain

Blockchain leverages various technologies:
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Networks: Decentralized networks for data distribution.
- Encryption Technology: Public key cryptography secures transactions.
- Consensus Algorithms: Mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) validate transactions.
- Smart Contracts: Automated, self-executing contracts with predefined rules.
Types of Blockchains
Blockchains are classified into three types:
- Public Blockchains: Permission-less and open to all.
- Private Blockchains: Restricted to specific participants.
- Consortium Blockchains: Controlled by a group, requiring permission for access.
Real World Applications of Blockchain
Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain is transforming various industries:
- Financial Services: Payments, remittances, and securities transactions.
- Retail: Point management and loyalty programs.
- Real Estate: Property transactions and title verification.
- Logistics: Supply chain management and traceability.
- Healthcare: Electronic medical records and prescription management.
- Entertainment: Ownership and copyright management of artworks and music.
The Blockchain Smartphone

A blockchain smartphone integrates blockchain technology into its operating system. These phones, whether using Android, a proprietary OS, or a hybrid, come equipped with a hardware wallet for managing crypto assets. Apart from this feature, blockchain smartphones function like regular smartphones, with standard features such as cameras and email capabilities.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a game-changer, offering secure, decentralized, and cost-effective solutions across various sectors. Its robust security measures and wide-ranging applications make it a cornerstone of modern technological advancements.
Also Check
- Top 10 Best VPN Providers 2024
- Privacy Enhancing Computing
- Human Augmentation
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)

1 Comment
Pingback: Will Cryptocurrency Be The Future Of Money In 2024 - 2025 Will Cryptocurrency Be The Future Of Money In 2024 - 2025